import heapq
def solution(land, height):
N = len(land)
d = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
board = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]
que = [(0, 0, 0)]
answer = 0
while que :
cost, h, w = heapq.heappop(que)
if board[h][w] : continue
board[h][w] = 1
answer += cost
cur_height = land[h][w]
for next_h, next_w in [[h+dh, w+dw] for dh, dw in d if 0 <= h+dh < N and 0 <= w+dw < N] :
next_height = land[next_h][next_w]
next_cost = n_cost if (n_cost := abs(cur_height - next_height)) > height else 0
heapq.heappush(que, (next_cost, next_h, next_w))
return answer
heapq
전형적인 level 3 수준의 문제지만 한번 꼬았다. 바로 사다리 설치비용을 구하는것이다. 모든 방을 방문하는데 드는 비용을 구하는 문제였으면 훨씬 쉬웠겠지만, 사다리 설치비용 을 구하기란 쉬워보이지만 매우 까다롭다. 알고리즘은 이렇다
BFS탐색을 진행하되, 비용이 가장 적게드는 자식부터 먼저 탐색을 진행
- heapq를 이용
이것이 핵심이다. 그 외에는 나머지 BFS와 똑같다.

(1, 1) -> (1, 2) | (2, 1) -> (3, 1) | (2, 2) | (1, 3) 이런식으로 BFS가 진행될 때 사다리 설치가 필요한 칸들은 제껴놓고 진행하는 방식이다. 좀 이해가 팍 될만한 비유를 들자면
SJF알고리즘을 이용한다고 생각하면된다. 사다리를 써야하는 경우를 기아현상으로 굶겨버리고 필요없는 경우들 부터 해결을 해나가는 것이다.
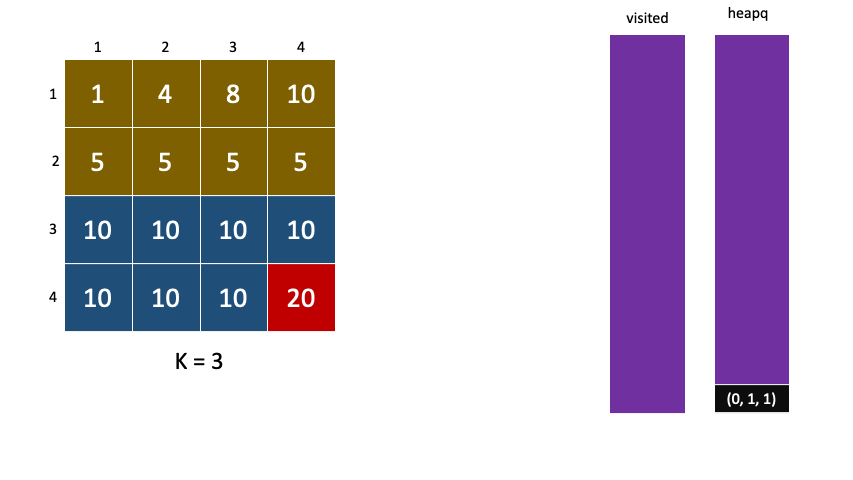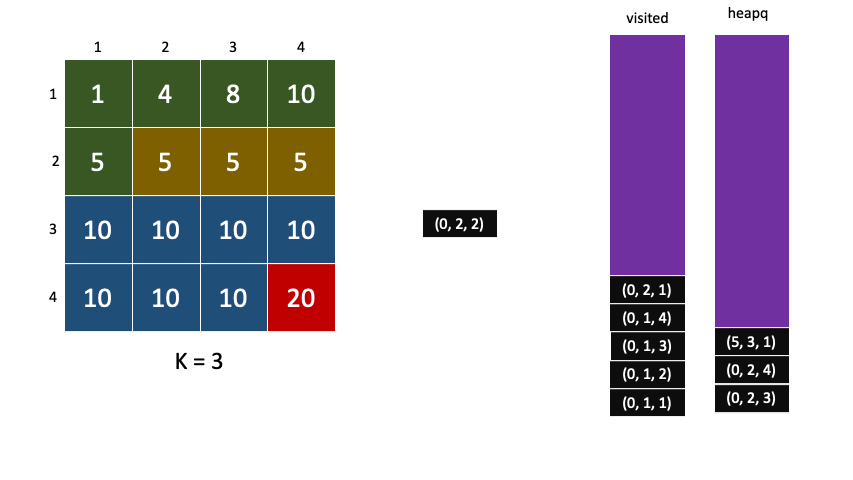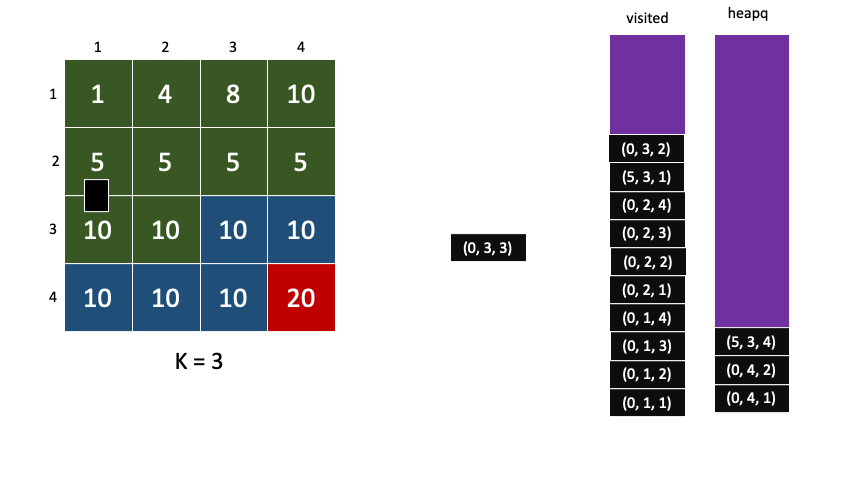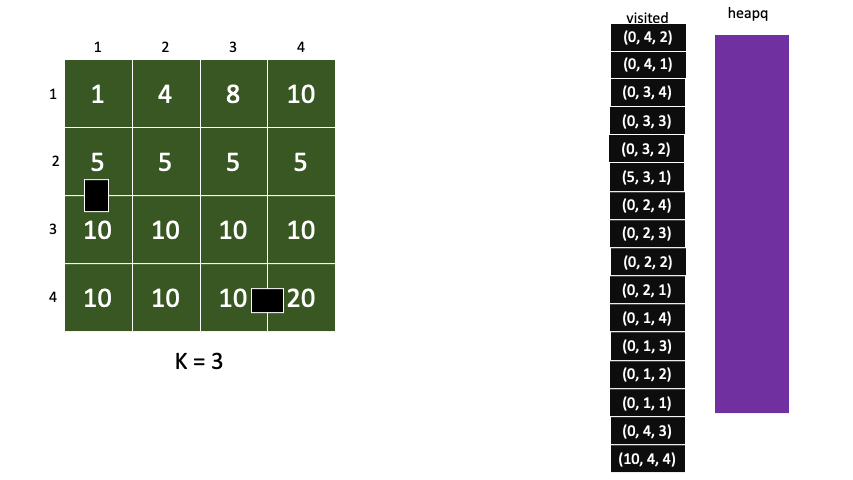
이렇게 비용이 높은 자식은 기아현상은 기아현상이 생겨 계속 뒤로 밀려나게된다.
import heapq
def solution(land, height):
N = len(land)
d = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
board = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]
que = [(0, 0, 0)]
answer = 0
while que :
cost, h, w = heapq.heappop(que) # heappop
if board[h][w] : continue # 이미 방문된 노드
board[h][w] = 1 # 방문처리
answer += cost # 사다리가 생길때만 사다리 비용이 추가됨
cur_height = land[h][w]
for next_h, next_w in [[h+dh, w+dw] for dh, dw in d if 0 <= h+dh < N and 0 <= w+dw < N] :
next_height = land[next_h][next_w]
next_cost = n_cost if (n_cost := abs(cur_height - next_height)) > height else 0 # 사다리 비용 추가하는 코드
heapq.heappush(que, (next_cost, next_h, next_w))
return answer