import re
from itertools import permutations
def check(banned_permutations, patterns) :
for pattern, ban_id in zip(patterns, banned_permutations) :
if not pattern.fullmatch(ban_id) :
return False
return True
def solution(user_id, banned_id):
answer = []
patterns = [re.compile(x.replace('*', '.')) for x in banned_id]
for banned_permutations in permutations(user_id, len(banned_id)):
if check(banned_permutations, patterns) and set(banned_permutations) not in answer:
answer.append(set(banned_permutations))
return len(answer)
풀이
이문제는 사실 쉬워서 설명을 하기가 오히려 좀더 어렵다. 대신 정규식 fullmatch를 알아야한다.
banned_id의 패턴*의 역할을 하는것이 정규식에서.이다.'f*od*'\(\rightarrow\)'f.od.'로 바꾼 후fullmatch로 패턴에 대응되는 단어들을 찾을 수 있다.
주의사항
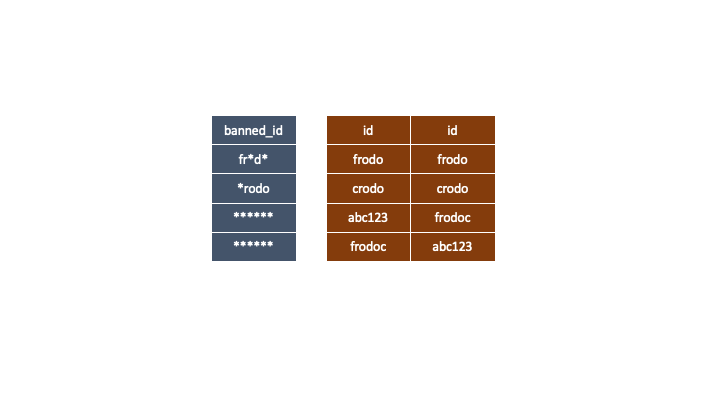
갈색 2개의 제제 아이디는 같은 경우로 보기 때문에 중복 제거를 꼭 해주어야한다.
import re
from itertools import permutations
def check(banned_permutations, patterns) :
for pattern, ban_id in zip(patterns, banned_permutations) :
if not pattern.fullmatch(ban_id) : # 패턴과 순열이 하나라도 대응되지 않으면 False
return False
return True # 패턴과 순열이 모두 대응되야 True
def solution(user_id, banned_id):
answer = []
patterns = [re.compile(x.replace('*', '.')) for x in banned_id] # 패턴 compile
for banned_permutations in permutations(user_id, len(banned_id)): # id 목록 banned_id 만큼 순열
if check(banned_permutations, patterns) and set(banned_permutations) not in answer:
# 1대1 대응 체크 및 중복 체크
answer.append(set(banned_permutations))
return len(answer)