가짜 해밀토니안
다시 쓸예정. 참고ㄴㄴ
코드
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(400000)
from collections import defaultdict
def set_depth_subtree(node, prev) :
sub_trees, depths = [], []
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
set_depth_subtree(child, node)
sub_trees.append((sub_tree[child], child))
depths.append((depth[child], child))
depth[node] = max(depth[node], depth[child] + 1)
sub_trees.sort(reverse=True)
depths.sort(reverse=True)
if len(sub_trees) >= 2 :
if sub_trees[0][1] != depths[0][1] : sub_tree[node] = sub_trees[0][0] + depths[0][0] + 1
else : sub_tree[node] = max(sub_trees[0][0] + depths[1][0] + 1, sub_trees[1][0]+depths[0][0] + 1)
elif len(sub_trees) == 1 : sub_tree[node] = sub_trees[0][0] + 1
def DFS(node, prev, height) :
global answer
sub_trees, depths = [], []
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
sub_trees.append((sub_tree[child], child))
depths.append((depth[child], child))
sub_trees.sort(reverse=True)
depths.sort(reverse=True)
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
next_height = height + 1
if depths[0][1] != child :
next_height = max(next_height, depths[0][0] + 2)
elif len(depths) >= 2 and depths[0][1] == child :
next_height = max(next_height, depths[1][0] + 2)
DFS(child, node, next_height)
if (len(sub_trees) >= 3) :
answer = max(answer,
sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[1][0]+height,
sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[2][0]+depths[1][0]+1,
sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[1][0]+depths[2][0]+1)
elif (len(sub_trees) == 2) :
answer = max(answer, sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[1][0]+height)
def solution(t):
global answer, N, graph, sub_tree, depth
N = len(t) + 1
graph = defaultdict(list)
sub_tree, depth = [1]*N, [1]*N
answer = 0
for v1, v2 in t:
graph[v1].append(v2)
graph[v2].append(v1)
set_depth_subtree(0, -1)
DFS(0, -1, 1)
return answer
우선 가짜 해밀토니안 경로를 만족하는 그래프는 어떤 형태의 그래프인지 알아야합니다.
가짜 해밀토니안 경로 정의
- 경로가 그래프 상의 모든 점을 최소 1번, 최대 2번 방문해야 합니다.
같은 점을 두번넘게 방문 하지 않으려면

- 메인 경로가 하나 있고, 그 경로 상에 있는 모든 노드들에 대해서, 해당 노드에서 출발하는 일자형으로 뻗은 서브 경로가 최대 1개 있는 그래프
이런 모양을 트리형태로 바꿔보면
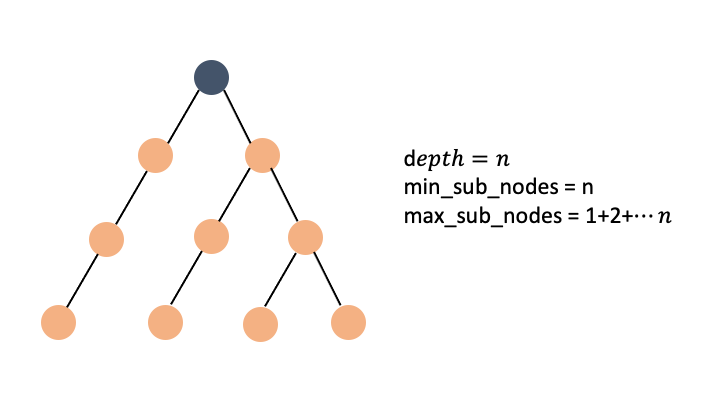
가짜 해밀토니안 경로를 만족하는 트리는 이런 이진트리 형태가 됩니다.
제한 사항
- v1과 v2는 서로 다른 수입니다.
- t는 항상 트리 형태로만 주어집니다.
입력값인 t 는 항상 트리 형태로 주어진다고 했습니다. 문제를 요약해보면

무작위로 주어진 트리형태의 그래프를 이런식으로 바꿔서 갯수를 return 하라는 문제가 됩니다. 하지만 큰 문제가 있습니다.
문제
- Degree가 4이상인(자식이 3개 이상인) 노드는 어떻게 처리해야 하는가?
- 어떤
node를 선택해야 가장 큰 해밀토니안 트리가 되는가?
생각만해도 머리가 깨질꺼같은 이 두가지 문제를 해결해야 합니다. 그냥 생각없이 계산한다면 n 개의 node 들로 이루어진 그래프일 경우 최악의 경우에는 \(n*2^{n}\) 번의 계산을 해야합니다.
가짜 해밀토니안 Tree
우선 Degree가 4개 이상인 노드를 어떻게 처리할지 생각해봅시다.

가짜 해밀토니안 tree의 모든 node 의 갯수는 Depth + num_sub_tree + 1 로 이루어져 있습니다. 그렇다면 주어진 그래프 t 에서 가장 큰 tree를 뽑아내려면 **각 node 의 자식들 중 Depth와 num_sub_tree가 가장 큰 자식들을 선택해야합니다. **
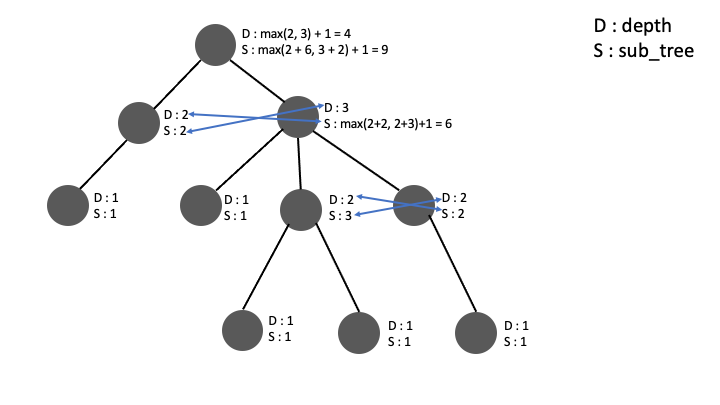
이런식으로 트리의 각 노드마다 Depth 와 sub_tree 갯수를 저장해가며 가장 큰 sub_tree 를 가지게 만들어줍니다.
def set_depth_subtree(node, prev) :
sub_trees, depths = [], [] # 자식들의 깊이와 sub_tree 노드 갯수가 저장될 리스트
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
set_depth_subtree(child, node) # leaf로 들어가는 DFS
sub_trees.append((sub_tree[child], child)) # node의 자식의 sub_tree 갯수 append
depths.append((depth[child], child)) # node의 자식의 depth append
depth[node] = max(depth[node], depth[child] + 1) # node의 depth 최신화
sub_trees.sort(reverse=True) # sub_tree 내림차순 정렬
depths.sort(reverse=True) #depth 내림차순 정렬
if len(sub_trees) >= 2 : # 자식이 2개 이상일 때
if sub_trees[0][1] != depths[0][1] : # depth가 가장 큰 node와 sub_tree가 가장 큰 node가 다를 때
sub_tree[node] = sub_trees[0][0] + depths[0][0] + 1
else : #depth가 가장 큰 node와 sub_tree가 가장 큰 node가 같을 때
sub_tree[node] = max(sub_trees[0][0] + depths[1][0] + 1, sub_trees[1][0]+depths[0][0] + 1)
elif len(sub_trees) == 1 : sub_tree[node] = sub_trees[0][0] + 1
def solution(t):
global answer, N, graph, sub_tree, depth
N = len(t) + 1
graph = defaultdict(list)
sub_tree, depth = [1]*N, [1]*N
answer = 0
for v1, v2 in t: # tree 그래프 생성
graph[v1].append(v2)
graph[v2].append(v1)
set_depth_subtree(0, -1) # 임의의 노드에서 시작, 0 아니어도 상관없음
return answer
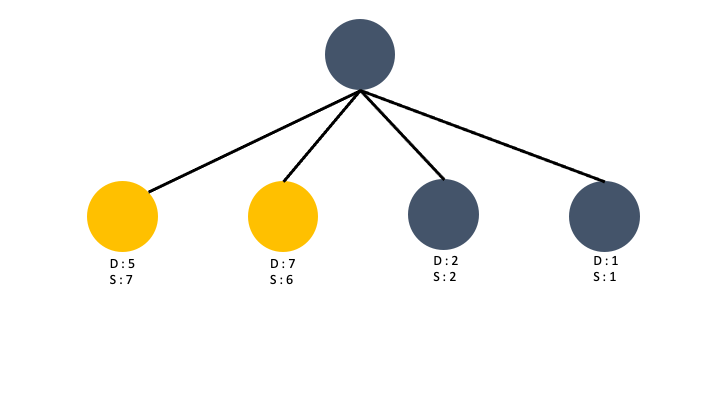
이렇게 Depth 가 가장 큰 노드와 Sub_tree 가 가장 큰 노드가 서로 다르면 그 둘을 선택하면 되지만
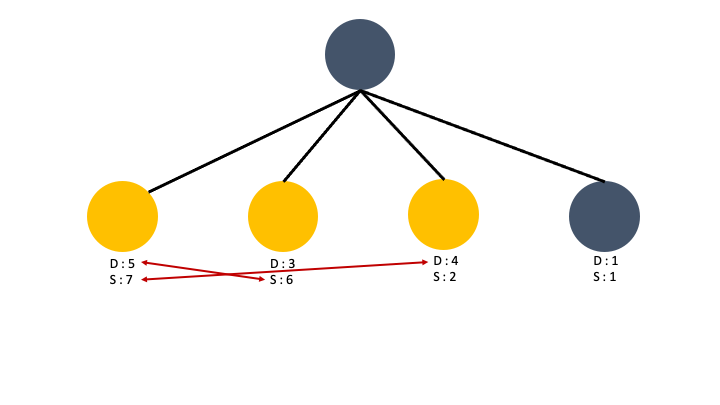
한 노드가 Depth 와 Sub_tree 둘다 가장 크다면 max(가장 큰 깊이 + 차선 서브트리, 가장 큰 서브트리 + 차선 깊이) 를 해주어야 합니다.
이렇게 임의의 노드를 기준으로 구성된 트리의 sub_tree 와 depth 정보들을 저장한 리스트를 DFS로 만들어 줍니다.
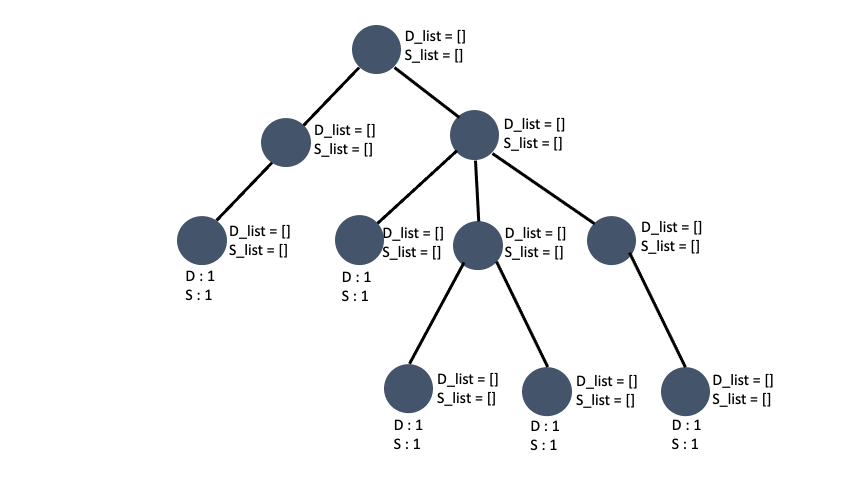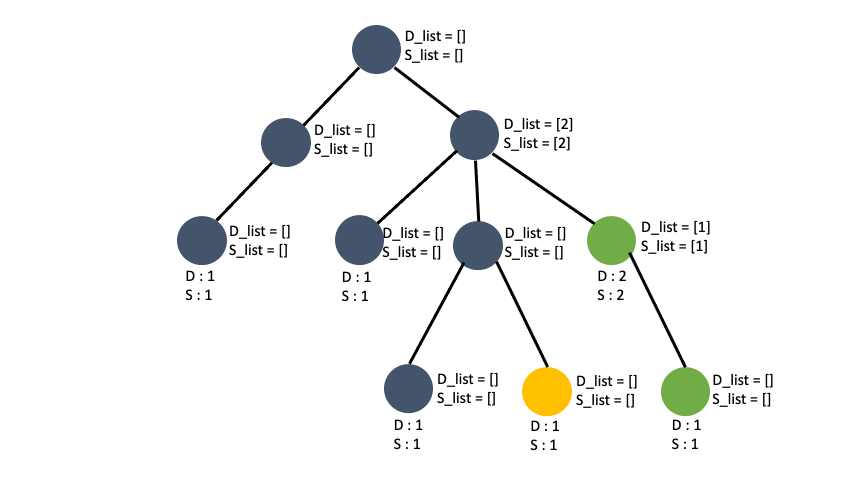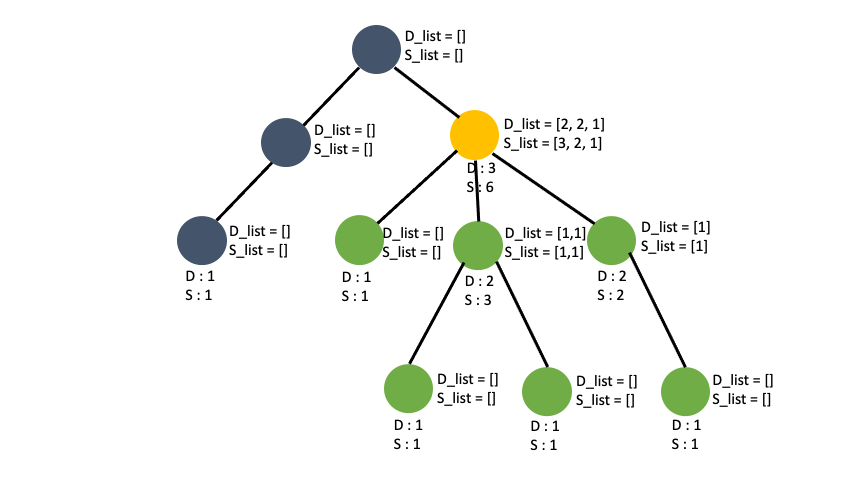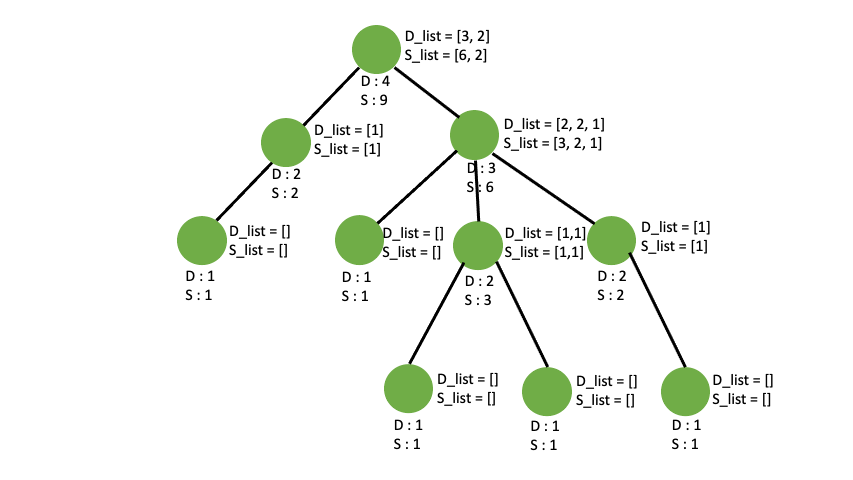
최대 subtree 값을 가지는 node 찾기
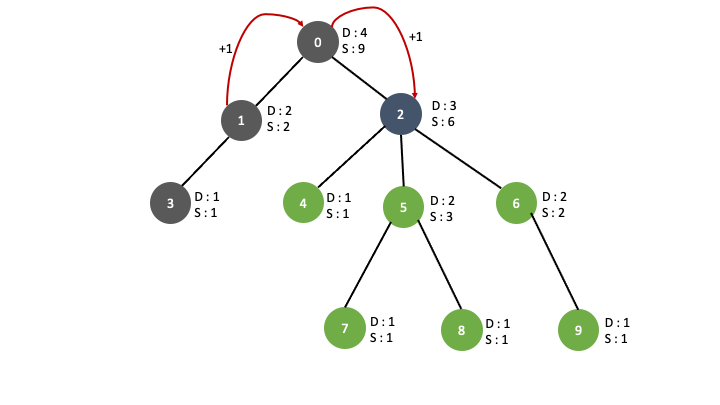
임의의 노드를 기준으로 트리를 완성시키고 각 노드를 취했을 때 얻을 수 있는 최대 depth, sub_tree를 구했습니다. 임의로 잡은 노드이기 때문에 그 트리의 root 의 sub_tree 갯수가 입력값 t 그래프의 갯수의 최대 sub_tree 인지 장담할 수 없습니다. 예를들면 이런 케이스가 있습니다.
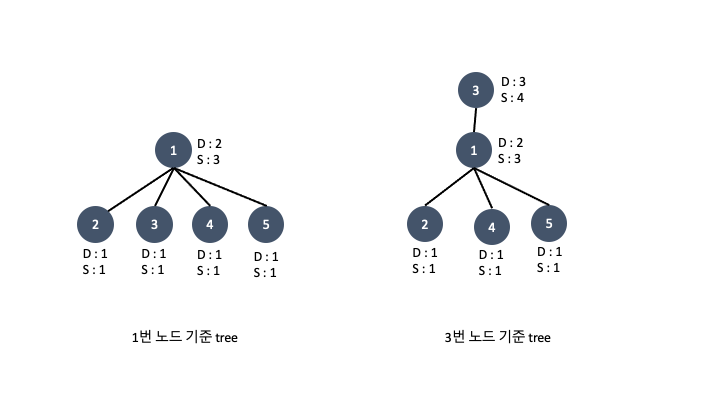
1번 노드를 기준으로 tree를 구성했을 때와 3번 노드를 기준으로 tree를 구성했을 때 root 의 sub_tree 의 갯수가 차이가 납니다. 그렇다고 **전체 노드에 대해서 DFS를 시행하면 중복된 depth 와 sub_tree 를 구하는 경우가 생기므로 시간초과나 런타임에러가 뜹니다. **
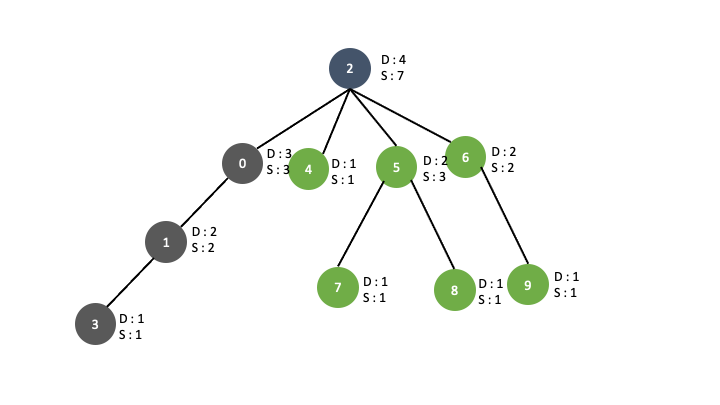
우선 가짜 해밀토니안 트리에서 노드하나를 떼서 봅시다.
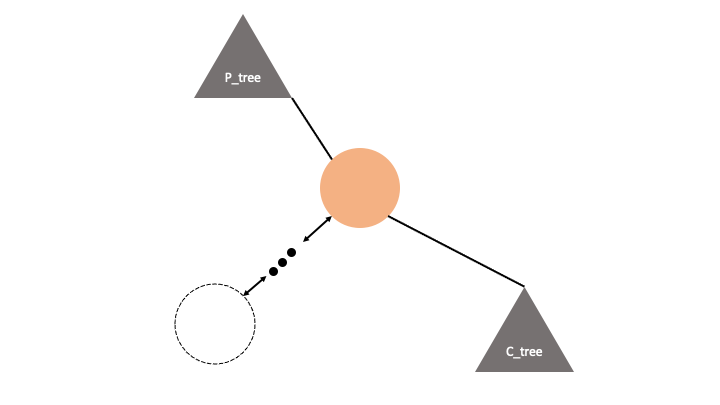
우리는 이 트리의 상태를 조금 다른 시각으로 볼 수 있습니다.
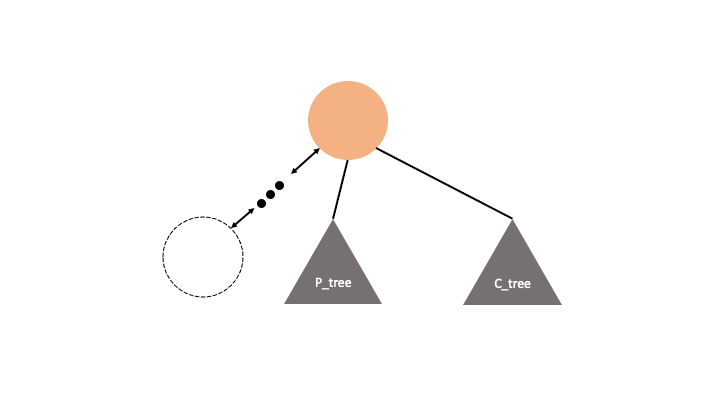
자기자신의 위쪽 sub tree를 아래쪽으로 내려서 마치 그 노드를 root 인것마냥 볼 수 있습니다.
그렇다면 내린 sub tree의 depth 와 sub_tree 의 갯수만 알면 전체 sub_tree 의 갯수를 알 수 있습니다.
height
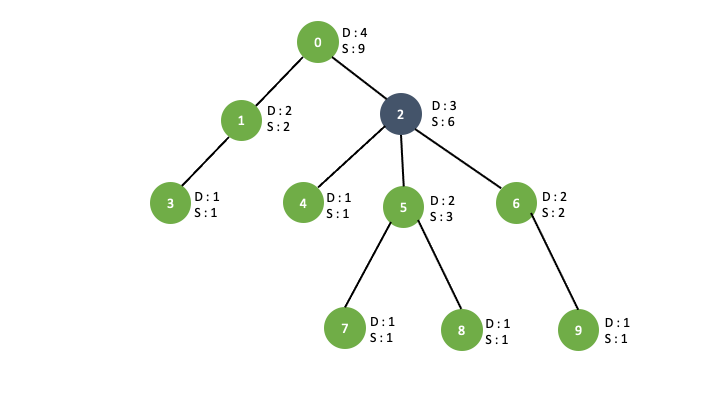
이미 0번을 루트로 만들어진 tree에서 2번 노드를 루트로 본다면, 0번 노드의 depth 는 max(0번 노드의 자식 중 2번 노드를 제외한 나머지 자식들의 높이) + 2가 됩니다. +2 가 되는 이유는
sub_tree 또한 마찬가지로 max(0번 노드의 자식 중 2번 노드를 제외한 나머지 자식들의 sub_tree) 이지만 구할 필요가 없습니다. depth 나 sub_tree 둘중 하나만 구하면 되는데 그 이유는 DFS 특성상 모든 자식 노드들에 돌아가며 depth, sub_tree 구하는 수행을 하기 때문에 자식노드의 부모 노드의 depth 와 sub_tree 를 계산하면 중복 계산이 일어납니다. 이거는 그림이나 말로 설명하기 어려우니 상상을 하며 코딩을 하시면서 이해하시길 바랍니다.
depth 계산이 더 쉬우므로 부모노드의 depth, 즉 height 를 구한뒤 기존 depth 와 height 중 큰것으로 depth 를 최신화 시켜주면 됩니다.
def DFS(node, prev, height) :
global answer
sub_trees, depths = [], []
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
sub_trees.append((sub_tree[child], child))
depths.append((depth[child], child))
sub_trees.sort(reverse=True)
depths.sort(reverse=True)
# node의 자식노드들에 대해서 높이 구하는 반복문
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
next_height = height + 1
if depths[0][1] != child :
next_height = max(next_height, depths[0][0] + 2)
elif len(depths) >= 2 and depths[0][1] == child :
next_height = max(next_height, depths[1][0] + 2)
DFS(child, node, next_height)
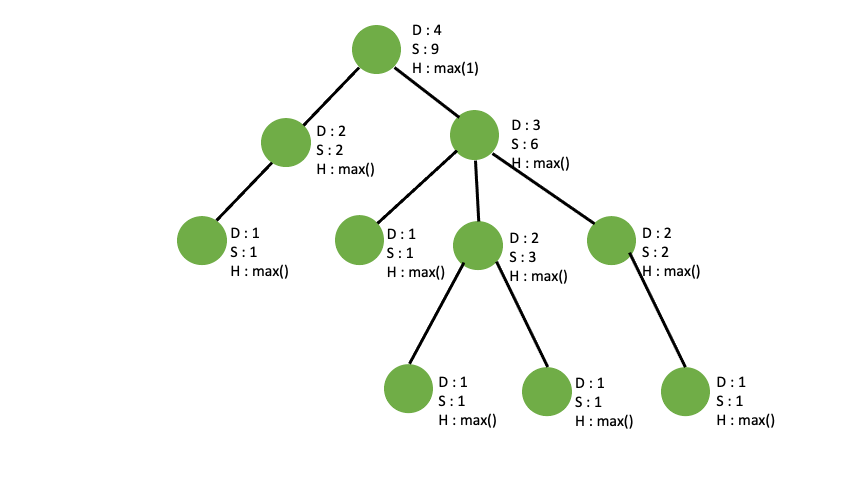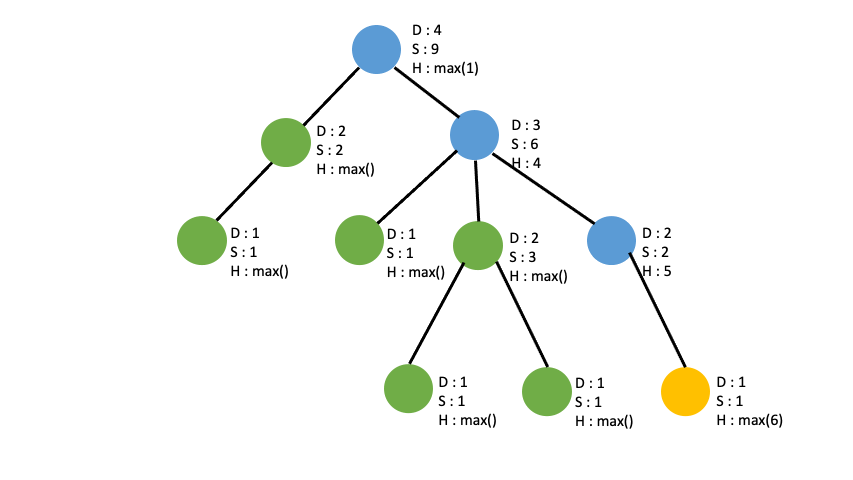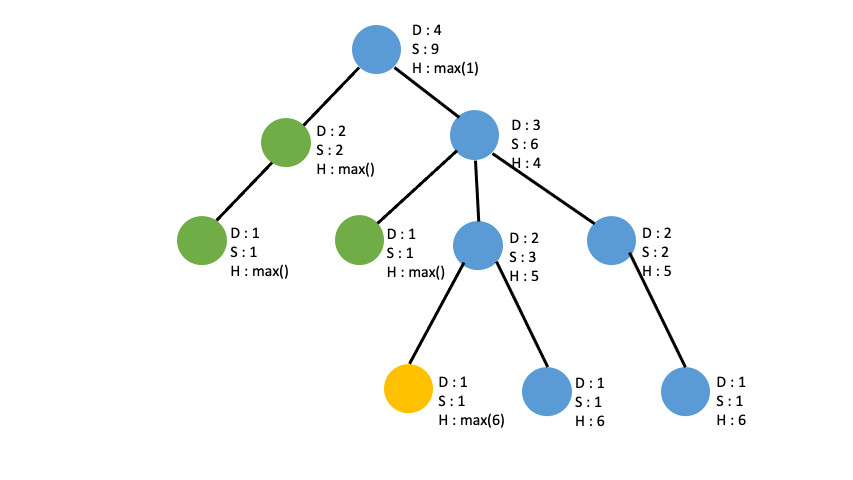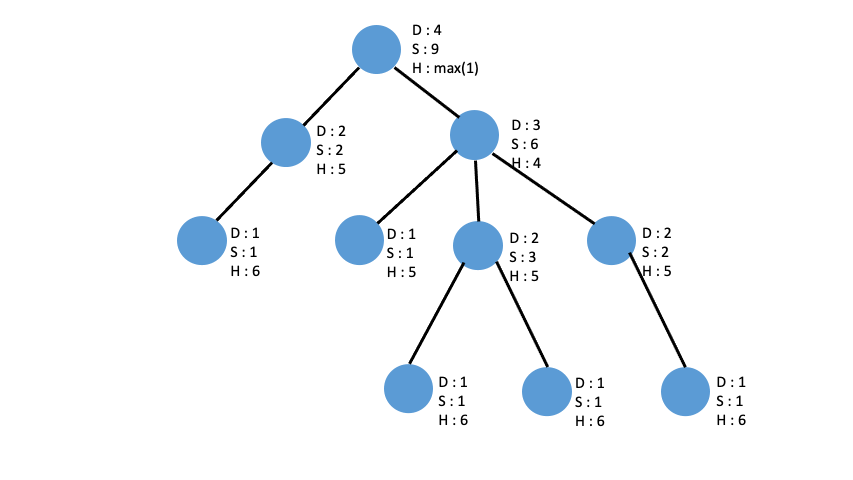
answer

각 node들에 대해서 height, depth, sub_tree 를 구했으니 가장 큰 값을 만드는 sub_tree 2개와 depth 를 찾으면 됩니다.
def DFS(node, prev, height) :
global answer
sub_trees, depths = [], []
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
sub_trees.append((sub_tree[child], child))
depths.append((depth[child], child))
sub_trees.sort(reverse=True)
depths.sort(reverse=True)
for child in graph[node] :
if child == prev : continue
next_height = height + 1
if depths[0][1] != child :
next_height = max(next_height, depths[0][0] + 2)
elif len(depths) >= 2 and depths[0][1] == child :
next_height = max(next_height, depths[1][0] + 2)
DFS(child, node, next_height)
# 정답을 찾는 부분
# 각 노드들에 대해서 최대값을 return 하는 후보들중에서 max값 구하기
if (len(sub_trees) >= 3) :
answer = max(answer,
sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[1][0]+height,
sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[2][0]+depths[1][0]+1,
sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[1][0]+depths[2][0]+1)
elif (len(sub_trees) == 2) :
answer = max(answer, sub_trees[0][0]+sub_trees[1][0]+height)